Database Preferences
The database preferences screen is where you set up the initial and main properties for the database.
You can view the first part of the video Adventure Works in 5 Minutes to see a walkthrough of the Database Preferences.
Below we cover the following topics:
To access the Database Preferences you would click on the gear next to the database name in the advanced Database view.
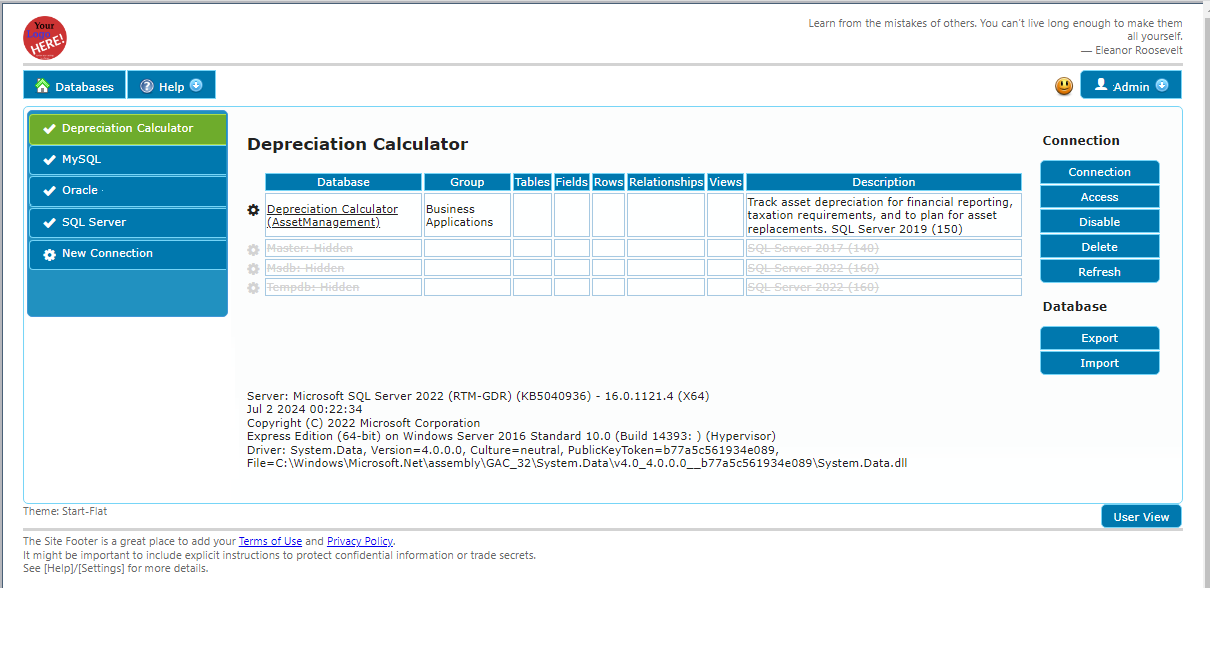
Main Database Preferences
The main preferences cover several areas from the main caption to the security.
The following settings are available on the main tab
- Caption: The Display name of the database as seen in the User and Advanced menu.
- Description: Room for a short description to give a user more context.
- Group: The Group name under which to place this database. The group name is explained in more detail in the Creating Database Groups section below.
- Record Locking: The ability to automatically lock the current record so that users can edit it without the fear of losing data, or having it changed without consent. Record Locking.
- Grid Editing: The ability to edit the data in a grid to allow for more efficient entry.
- Startup View: What you want to be seen first by your users.
Field Defaults
- Date Format: Set the default format for any displayed dates.
- Label Position: The default position of field labels.
Site Layout
- Custom CSS File: Allows you to specify a custom CSS file that is loaded when this database is in view. Various elements including Tables, Layout Groups, Fields, etc.. can have a custom CSS class name assigned so that it becomes easier to make custom layout changes.
- Logo File: Where you put the URL for the logo.
- Theme: Select a specific UI theme for a database. If a theme is selected then a user will not be able to pick a different one.
- Hidden: Primarily used to hide System Databases to which a user might have access as part of a connection.
Creating Database Groups
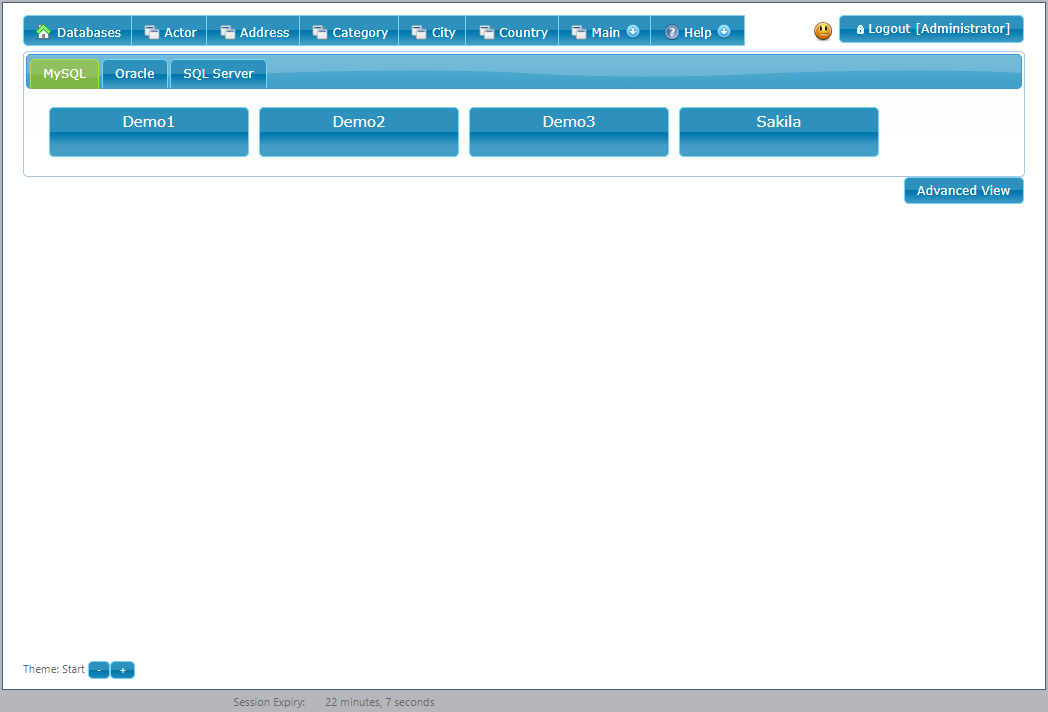
In the Advanced database view shown at the top of this page, the databases are organized by connection and server which makes sense for administrators.
In the User database view shown to the right, the databases are organized into tabs based on the group that is assigned on the main tab of the Database Preferences screen.
This allows the various databases to be organized into groups that the business understands such as by department or function.
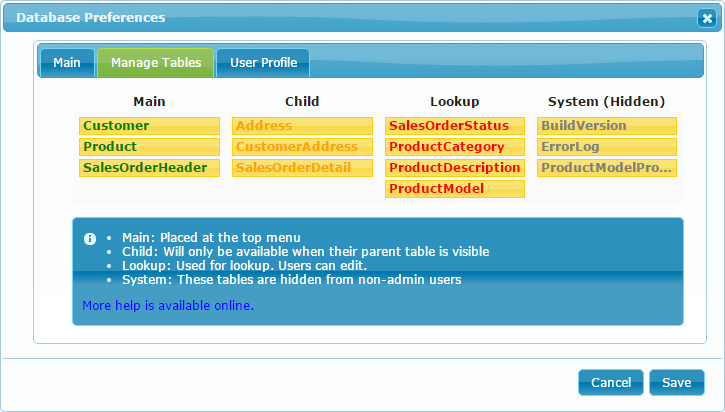
Manage Tables
The Manage Tables tab is where you do the initial setup of how your tables will appear to the user.
There are four columns in the Manage Tables tab which correspond to the four different ways that dbFront understands tables.
Main Tables
The main tables represent the primary entry points for a database. If there are only a few main tables then they will all appear individually in the menu at the top of the screen. If there are too many then the first number will appear in the top menu and the complete set will appear grouped in a menu named "Main".
The order (sequence) of the tables at the top of the screen is determined by the table order in the Main column.
Child Tables
Tables that are designated as child tables won't be accessible from any menu directly but they will appear in an appropriate tab when their parent tables are loaded up. The tab label will include the name of the field in the tab label so that it is clear how the child table is related.
When the child table is shown, the field(s) that are part of the relationship to the parent won't appear on the child tab. By definition, these fields will have the same values as the parent table, and so showing these values would be a waste of screen space.
Lookup Tables
Tables that are marked as lookup tables won't be included in the normal flow of the application except when they are needed as a lookup source. Users will still have the ability to open these tables from the "Lookup" menu.
System (Hidden) Tables
The System tables collection covers all other tables. Tables in this group won't be accessible to any user except for when they are used as a lookup source and even then, the users can only see what is made available in the dropdown field.
Administrators will still have full access to these tables via a menu named "System"
User Profiles
User Profiles are part of the security features in dbFront. You can use the requirement for a Database Profile to restrict or manage user access to individual databases. For more details see: User Profiles.
Next Step
The next step is to open the database and start updating the table and field preferences as needed